The world of digital advertising can seem complex, especially when delving into the intricacies of ad trafficking. This process, crucial for launching successful digital ad campaigns, involves a series of steps from initial ad creation to final deployment and reporting. This article serves as a comprehensive guide, demystifying the ad trafficking process and providing a clear, step-by-step roadmap for anyone looking to understand or manage online advertising campaigns more effectively. Whether you’re a seasoned marketing professional or new to the field, understanding the fundamentals of ad trafficking is essential for maximizing your advertising ROI and reaching your target audience. We’ll cover the core concepts that will help you understand how online ads are managed and published across different platforms and devices.
This guide will walk you through each stage of the ad trafficking process, from selecting the right ad server and understanding its functionalities to the technical aspects of tagging and creative implementation. We’ll also explore the importance of quality assurance (QA) and reporting to ensure optimal performance and accurate data collection. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a solid understanding of the essential elements involved in launching and managing a successful digital advertising campaign, empowering you to make informed decisions and optimize your marketing strategies for better results on a global scale. Understanding these steps will enable you to better strategize your campaigns and take action based on insightful data.
What is Ad Trafficking and Why is it Important?
Ad trafficking is the process of managing and implementing digital advertising campaigns within an ad server. It involves uploading creative assets, configuring targeting parameters, and generating ad tags to be placed on publisher websites or within mobile applications.
In simpler terms, it’s the act of taking all the components of an ad campaign – the banner ads, videos, and specified audience – and making sure they appear on the correct websites, to the right people, and at the scheduled times.
Why is ad trafficking important? It ensures the accurate and efficient delivery of digital ads, directly impacting campaign performance. Proper trafficking minimizes errors, prevents wasted ad spend, and maximizes ROI. Without meticulous ad trafficking, campaigns can fail to reach their intended audience, leading to poor results and lost revenue. Moreover, effective ad trafficking provides accurate data for campaign analysis and optimization.
The Key Roles and Responsibilities in the Ad Trafficking Process
Effective ad trafficking requires a collaborative effort from various individuals and teams. Understanding their roles and responsibilities is crucial for a smooth and successful campaign launch. Here’s a breakdown of the key players:
- Ad Operations Team: Responsible for the overall execution of the ad campaign, including trafficking, QA, and reporting.
- Campaign Managers: Oversee the strategic planning and performance of ad campaigns. They work closely with the ad operations team to ensure campaign goals are met.
- Traffickers: The individuals directly responsible for implementing the ad tags in the ad server, ensuring correct targeting and delivery. Their role is highly technical.
- Creative Team: Develops and provides the ad creatives (banners, videos, etc.) to the ad operations team.
- Sales Team: Sells advertising space to clients and provides campaign details.
Clear communication and well-defined responsibilities among these roles are essential to minimize errors and maximize campaign effectiveness. Each team relies on the other for accurate information and timely execution.
A Step-by-Step Guide to the Ad Trafficking Workflow
The ad trafficking workflow is a sequential process involving several key steps to ensure digital ad campaigns are launched and managed effectively. Understanding this workflow is crucial for successful campaign execution.
- Campaign Setup: Define campaign objectives, target audience, budget, and flight dates.
- Creative Submission: Receive ad creatives (banners, videos, etc.) from the creative team.
- Ad Server Configuration: Input campaign details and creative assets into the ad server.
- Tag Generation: Generate ad tags for each creative and placement.
- Tag Implementation: Send ad tags to the publisher or website for placement on their site.
- QA Testing: Thoroughly test ad tags to ensure proper functionality, tracking, and appearance.
- Campaign Launch: Activate the campaign within the ad server.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor campaign performance and make necessary adjustments to improve results.
Each step requires careful attention to detail to minimize errors and maximize campaign impact. Proper execution of each stage contributes to the overall success of the digital advertising campaign.
Setting Up Ad Campaigns in an Ad Server

Once your campaign is planned and creative assets are ready, the next crucial step is setting up the campaign within an ad server. This involves configuring various parameters to ensure your ads are displayed correctly to the intended audience.
Campaign Setup Steps:
- Create a New Campaign: Within your chosen ad server (e.g., Google Ad Manager, Adform, Sizmek), initiate a new campaign.
- Define Campaign Objectives: Specify the goals of your campaign, such as brand awareness, lead generation, or website traffic.
- Set Targeting Criteria: Configure targeting parameters, including demographics, interests, geographic location, and device type, to reach your desired audience.
- Allocate Budget and Schedule: Determine the total budget for the campaign and set the start and end dates. Distribute the budget across different line items (ad groups) as needed.
- Configure Bidding Strategies: Select an appropriate bidding strategy (e.g., CPM, CPC, vCPM) and set bid values to optimize ad delivery.
- Upload Creative Assets: Upload your ad creatives (e.g., banner ads, video ads) in the required formats and sizes.
- Define Frequency Capping: Set frequency caps to limit the number of times an individual user sees your ads within a specified time period.
Accurate configuration is essential for effective campaign execution and optimal results. Double-check all settings before activating the campaign.
Generating and Implementing Ad Tags
The generation and implementation of ad tags are critical steps in the ad trafficking process. Ad tags are snippets of code that instruct web browsers or apps on where and how to display advertisements. These tags are typically generated within the ad server platform after an ad campaign is configured.
Generating Ad Tags:
- Select the appropriate ad unit and size.
- Configure any necessary targeting parameters (e.g., geographic location, demographics).
- Choose the tag type (e.g., JavaScript, Iframe).
- Generate the ad tag code.
Implementing Ad Tags:
- Copy the generated ad tag code.
- Paste the code into the designated area within the website’s or app’s HTML code. This is usually done by the publisher or web developer.
- Ensure the tag is placed correctly within the desired ad placement location.
Proper implementation ensures that the correct ad creative is displayed to the intended audience. Failure to implement ad tags correctly can result in ads not displaying, displaying incorrectly, or targeting the wrong audience.
Quality Assurance (QA) Testing for Ad Campaigns
Quality Assurance (QA) testing is a crucial stage in the ad trafficking process, ensuring that ad campaigns function correctly and deliver the intended user experience before launch. This phase involves a thorough examination of all campaign elements to identify and rectify any errors or discrepancies.
The primary objective of QA testing is to verify that ads are displaying correctly on designated websites and apps, tracking clicks and impressions accurately, and adhering to specified targeting parameters. This process helps to minimize wasted ad spend and maximize campaign effectiveness.
Key Aspects of QA Testing:
- Ad Creative Verification: Confirming that ad creatives render properly across different browsers, devices, and operating systems.
- Click-Through URL Validation: Ensuring that click-through URLs redirect users to the correct landing pages.
- Tracking Pixel Implementation: Verifying that tracking pixels are firing accurately to capture relevant data.
- Targeting Accuracy: Confirming that ads are being served to the intended audience based on demographic, geographic, and behavioral targeting criteria.
Effective QA testing involves using specialized tools and techniques to simulate user interactions and monitor campaign performance. This proactive approach helps to identify and resolve issues early on, preventing potential problems that could negatively impact campaign results.
Troubleshooting Common Ad Trafficking Issues
Even with meticulous planning, ad trafficking can encounter issues. This section provides guidance on resolving common problems efficiently.
Common Issues and Solutions:
- Discrepancies in Impressions/Clicks: Investigate potential tag implementation errors, caching problems, or discrepancies in time zones across platforms. Verify reporting methodologies.
- Ads Not Rendering: Check for broken ad tags, incorrect targeting parameters, or browser compatibility issues. Utilize browser developer tools to inspect network requests and console errors.
- Incorrect Creative Display: Confirm creative specifications are correct and that the correct creative is assigned to the appropriate ad slot. Clear browser cache to ensure the latest version is displaying.
- Reporting Errors: Validate data integrity by cross-referencing reports from the ad server, publisher, and any third-party tracking tools.
Debugging Tools: Leverage browser developer tools, ad server debugging consoles, and third-party tag validators to identify and diagnose issues promptly. Effective troubleshooting minimizes campaign downtime and maximizes performance.
Best Practices for Efficient and Accurate Ad Trafficking
To ensure efficient and accurate ad trafficking, several best practices should be implemented throughout the process. These guidelines help minimize errors, optimize campaign performance, and streamline workflow.
Standardization and Organization
Establish clear naming conventions for campaigns, ad groups, and creatives. A standardized approach ensures consistency and ease of identification. Implement a robust organizational system for all assets and documentation.
Attention to Detail
Meticulously review all ad specifications, including dimensions, file sizes, and landing page URLs, to prevent discrepancies. Double-check creative assets before uploading them to the ad server.
Regular Audits
Conduct periodic audits of active campaigns to identify and rectify any discrepancies or errors. Regularly review and update trafficking documentation.
Leverage Automation
Utilize automation tools and features within the ad server to streamline repetitive tasks, such as tag generation and reporting. This reduces the potential for human error and increases efficiency.
Continuous Training
Provide ongoing training to the ad trafficking team to keep them updated on the latest industry best practices and ad server functionalities. Encourage knowledge sharing and collaboration within the team.
Reporting and Analysis of Ad Campaign Performance
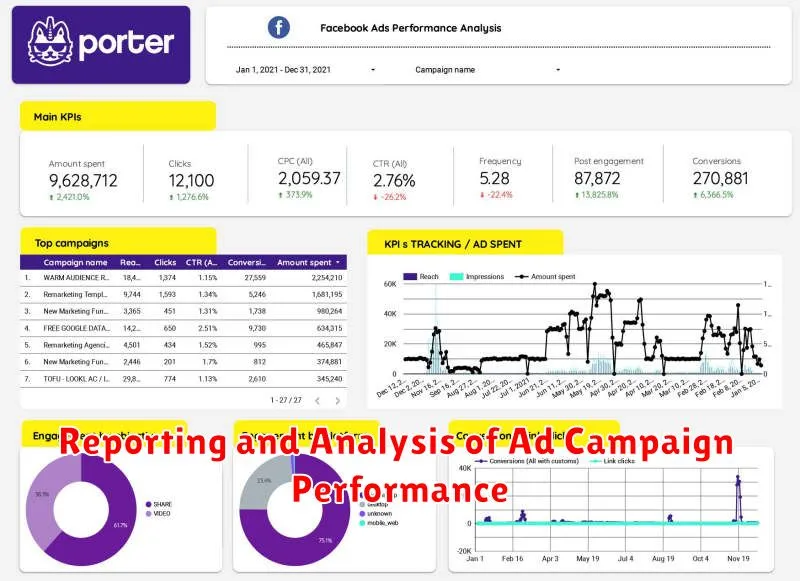
Reporting and analysis are crucial for understanding the effectiveness of ad campaigns and optimizing future strategies. Regularly monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) provides actionable insights into campaign performance.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track:
- Impressions: The number of times an ad is displayed.
- Clicks: The number of times users click on an ad.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of impressions that result in clicks (Clicks / Impressions).
- Conversions: The number of desired actions taken after clicking an ad (e.g., purchases, sign-ups).
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of clicks that result in conversions (Conversions / Clicks).
- Cost Per Click (CPC): The average cost paid for each click.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): The average cost paid for each conversion.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): The revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising.
Reporting Tools and Dashboards:
Utilize ad server reporting tools and dashboards to visualize campaign data and identify trends. These tools allow for custom reporting and segmentation of data for deeper analysis. Regular reporting should be established to track progress against goals and objectives.

